Rotational moulding compared to other production techniques

The plastics manufacturing industry has countless processes for the production of plastic products. In addition to rotational moulding, blow moulding and injection moulding are the most important ones.
Table of contents
Rotational moulding in a nutshell
Rotational moulding is a tension-free process of heating plastic powder in a mould to form a plastic product. In this production process, an aluminium or sheet steel mould is filled with thermoplastic powder (usually PE or PP) and sealed. The mould is heated in a large oven while being rotated on two axes placed perpendicular to each other. As a result, the molten material is pressed against the mould wall to obtain its shape.
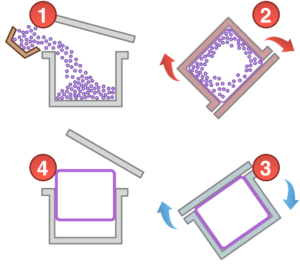
Next, the product is cooled and removed from the mould. The thermoplastic is processed free of tension, creating an impact-resistant product in almost any shape imaginable. Production series range from 100 to 5,000 products per mould per year and have a weight of 0,5 kg to 300 kg.
Rotational moulding vs blow moulding
Blow moulding is another highly popular production method that involves molten plastic being extruded in a preform. Pressurised gas, usually air, then presses the molten plastic into the mould until it cools and hardens. Once cooled, it can be removed from the mould.
Rotational moulding
+ Tension-free product
+ Low investment costs
+ Design freedom
Blow moulding
+ Short cycles
+ More material types possible
+ High degree of detailing possible
Rotational moulding vs vacuum moulding
Vacuum moulding involves plastic film being heated to the distortion temperature with e.g. an infrared oven. The heated film is stretched in or on a mould. A vacuum is created in between the surface of the mould and the plastic and as a result, the plastic is sucked into the shape of the mould. Next, the product undergoes a forced cooling process.
Rotational moulding
+ Tension-free product
+ Low investment costs
+ Design freedom
Vacuum moulding
+ Short cycles
+ More material types possible
+ High degree of detailing possible
Rotational moulding vs injection moulding
Injection moulding involves molten plastic being injected into a mould under high pressure. As a result of cooling, the plastic sets and the part is created. Injection moulding allows for the manufacturing of complex parts. Due to the high production costs of the mould, injection moulding is mostly suitable for larger production numbers.
Rotational moulding
+ Low investment costs
+ Thick walls possible
+ Easy to produce hollow products
Injection moulding
+ Short cycles
+ More material types possible

)